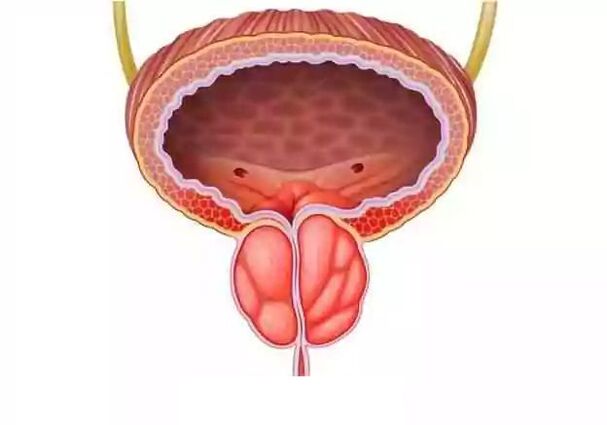
- Any inflammatory disease of the urinary system - cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis;
- Chronic bowel disorders - especially constipation, where men need to strain, and prostatitis, which is the organ's response to stress;
- Infections from distant lesions - severe forms of tonsillitis, pneumonia, influenza, when prostatitis is directly related to the penetration of infectious agents into glandular tissue;
- Frequent episodes of hypothermia or conversely hyperthermia may be associated with characteristics of work activities;
- Lack of regular sexual activity and physical activity - prostatitis can cause stagnation of prostate tissue secretions, which is usually the cause of prostatitis in men over 40 years old;
- Decreased immunity due to severe hormonal imbalance;
- Sexually transmitted infections - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia;
- Frequent urinary retention – an enlarged bladder puts tremendous pressure on the prostate;
- Injury to the pelvic area.
Types and course characteristics of male prostatitis
- Bacterial prostatitis - begins against the background of an infection penetrating the prostate tissue; the diagnosis of this type of prostatitis is more common in younger and older men;
- Congestive prostatitis - caused by a sedentary lifestyle, lack of regularity in men's sexual life, and pelvic injuries, etc. , often accompanied by infection, and then becomes mixed prostatitis;
- Calculous prostatitis - occurs due to untreated chronic disease; this type of prostatitis is more common in older men.
Symptoms and diagnosis of prostate inflammation
- Bacterial prostatitis - high body temperature, presence of blood or pus in the urine, problems with urination (thin, "dripping" urine), acute pain in the perineum, poor general health;
- Calculous prostatitis - weak or complete erection, blood in the urine, symptoms of prostatitis more common in men aged 50 and above;
- Congestive prostatitis - discomfort in the perineum and testicles, partial or complete absence of erection, improper urination.
- Symptoms of prostatitis in a 50-year-old man are weak erection and heaviness in the groin, but there may be no pain at all;
- The symptoms of prostatitis in a 30-year-old man are always severe, and the first sign is obstruction of urination: the enlarged prostate puts pressure on the bladder, and the man cannot go to the toilet at all;
- Men who are 60 years old may not experience prostatitis symptoms - at this age, prostatitis is often chronic, but the complete lack of erections can be disturbing.
- Rectal examination;
- Laboratory tests of prostate secretions;
- Analysis to identify/exclude sexually transmitted infections;
- Prostate ultrasound;
- Computed tomography of organs.
Treatment - general principles, duration of treatment
- NSAIDs and diuretics - prostatitis manifests itself as an invasion of the urinary process;
- Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants - prostatitis is accompanied by severe pain in the groin;
- Supports prostate function and alpha-blocker.
- Drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day - prostatitis is characterized by stagnation of secretions that need to be rapidly cleared from the tissues to relieve the load on the organ and reduce its swelling;
- Adhere to bed rest - treatment cannot be combined with physical activity, as this will irritate the organs and prostatitis will only progress, making treatment long and ineffective;
- Eliminate spicy, sour, fatty foods, alcohol from the diet - these are also irritants and will only aggravate prostatitis.
- Transurethral resection – the surgeon removes prostate tissue affected by prostatitis;
- Prostatectomy - Prostatitis poses a real danger to a man's life, so his prostate and seminal vesicles, along with their adjacent tissues, are completely removed.