prostatitis-Common diseases of reproductive age and elderly men.
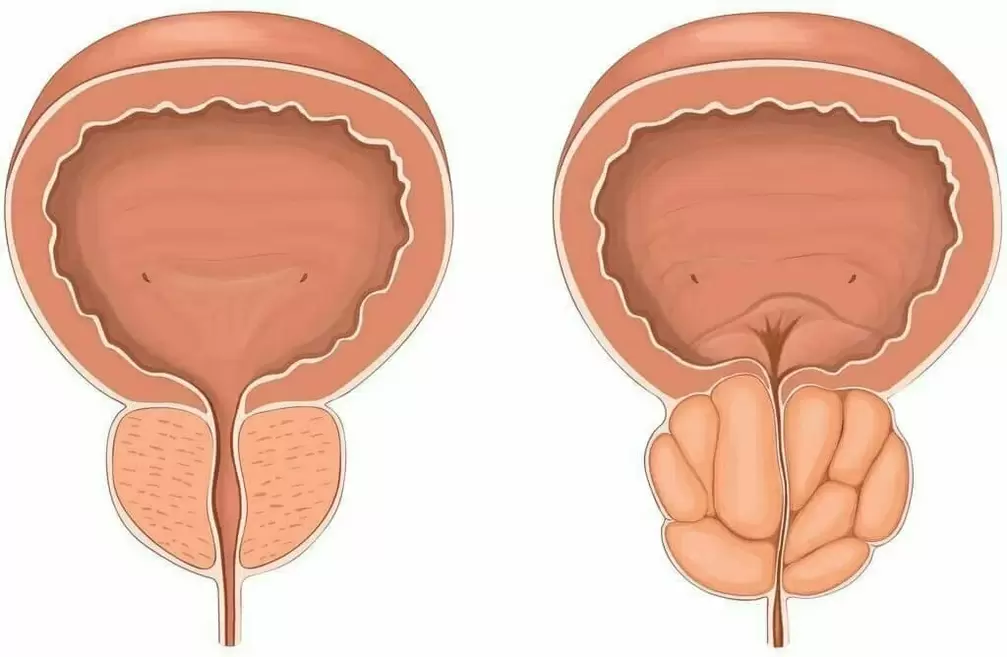
What is prostatitis? This is inflammation of the prostate in men, which is also called the prostate. The prostate is located near the bladder neck and is an important part of the male reproductive system. Inflammation of the prostate causes enlarged prostate. As a result, the urinary tract is compressed, the process of emptying the bladder becomes difficult, and other symptoms of discomfort appear. Therefore, in the case of prostate inflammation, it is not recommended to stop.
Symptoms and signs of prostatitis
Usually, men pay due attention to the manifestations of prostatitis very late. Even if we are talking about a disease, the clinical situation of each situation is individual. However, the initial symptoms of male prostatitis are roughly the same:
- Difficulty urinating. . . the compressed urethra under the inflamed prostate cannot pass urine well. The feeling of incomplete urination and the urge to urinate continuously are also the first signs of male prostatitis, and its symptoms will worsen in the future.
- Sexual disorder. . . These uncomfortable signs of prostate inflammation appear in men mainly because they violate the erection mechanism and weaken orgasm. In addition, symptoms of prostate inflammation include premature ejaculation.
- pain. . . One of the symptoms of male prostatitis is pain during urination and ejaculation. The typical symptom is persistent pain in the lower back.
- Nervousness. . . Symptoms of prostate inflammation include men's nervousness, because an enlarged prostate can cause some discomfort.
Causes of prostatitis
There are many reasons for prostatitis:
- Poor blood circulation. . . Due to lack of physical activity (sedentary and sedentary lifestyle), blood circulation may be impaired-this is a common cause of male prostatitis. Similarly, the reasons for the violation of the blood supply of the organs are overweight, minor pelvic injuries, and persistently low body temperature.
- infection. . . Infectious diseases often cause prostatitis. Due to sexually transmitted diseases and urinary system diseases, inflammatory processes in the rectum and complications after infectious diseases (tonsillitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis), it is easy to infect the prostate.
- Immune failure. . . The weakening of the body's protective function due to past diseases, stress, etc. , is usually the cause of male prostatitis or aggravation of existing diseases.
Types of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis develops rapidly with the rapid onset of characteristic symptoms. Chronic prostatitis usually appears gradually, and symptoms appear almost imperceptibly. This is a typical symptom for men over 55 years of age.
In addition, prostatitis is also classified by source:
- bacterial. It is most common at a young age, but in other types of diseases, such cases only account for 5-10%. Usually, due to the vulnerability of the human body to pathogenic bacteria, acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis will occur.
- Infectious. . . Infectious prostatitis not only occurs due to bacteria, but also due to fungi and protozoa, which distinguishes it from the types of bacteria. This type of disease can also occur in chronic and acute forms. One of its characteristic varieties is Chlamydia prostatitis.
- Purulent. . . Purulent prostatitis is one of the most serious types of infection, with purulent discharge and high fever. The course of the disease is acute, with new symptoms appearing at each stage.
- stone. . . Stone prostatitis is the result of a long-term chronic disease and is mainly observed in elderly men. This disease is characterized by the appearance of stones in the prostate.
- Stagnant. . . Non-bacterial prostatitis is caused by insufficient blood supply to the pelvic organs. Also called congestive prostatitis, it is usually chronic. Among all types, congestive prostatitis is the most common.
Why is prostatitis dangerous?
In any person, prostatitis without timely treatment can quickly become a chronic disease and cause serious consequences for reproductive health and general physical conditions. The most common complications of prostatitis include:
- Vasculitis. . . Seminal vesiculitis is the first thing that chronic prostatitis is dangerous for men. Vasculitis can occur without any symptoms, or it can be painful after urination, after sexual intercourse, and when pus and blood appear in semen.
- Posterior urethritis and colitis. . . The danger of prostatitis lies in the development of posterior urethritis and concomitant thalamicitis. Colitis is an inflammation of sperm that allows sperm to pass through. One of the symptoms of colitis is blood in semen.
- Prostate disease. . . The consequences of male prostatitis may be other more serious prostate diseases: abscesses, sclerosis, cysts and stones, adenomas, cancer. Compared with prostatitis, the treatment of these complications is more difficult and takes longer, and some of the consequences are irreversible.
- Sexual dysfunction. . . The consequence of excessive inflammation of the prostate may be problems in the genital area, including erectile dysfunction. Although yang ot caused by prostatitis can be cured, it is usually irreversible.
- Infertility. . . Since the reproductive system of the male body with prostatitis cannot perform its functions well, infertility is usually the result of chronic prostatitis. It all starts with deterioration of sperm quality and vas deferens patency.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
The diagnosis of male prostatitis begins in the first minute of the doctor’s appointment, because the patient’s main complaint is an important part of it. In addition, in order to identify diseases and their characteristics, other types of diagnostic procedures can be used:
- Physical examination. . . During the medical examination, a digital rectal examination will be used, which is performed through the anus and allows you to identify the size, shape, surface condition and other characteristics of the prostate. Since diagnosing prostatitis in this way is very simple, this is actually the first way to confirm the diagnosis.
- Laboratory research. . . The male prostatitis test is used to study blood, urine, semen, and prostate secretions. One of the most effective methods is to perform urinalysis for prostatitis (routine, bacteriology, cytology). In addition, for prostatitis, routine blood tests are required. In each case, the doctor will determine which tests should be performed for prostatitis and whether more in-depth research methods are needed.
- Non-invasive method. . . These are ultrasound, X-ray diagnosis and MRI.
Treatment of prostatitis
It is strongly recommended not to treat prostatitis by yourself. If a man does not know which doctor can treat prostatitis, you can consult a therapist. But usually all patients know that urologists specialize in the treatment of male prostatitis. You can also contact a therapist or surgeon, but only for the first visit.
Many patients face a natural question: can prostatitis be cured? It all depends on the form of the disease. But in any case, the diagnosis and treatment of male prostatitis are necessary when the first warning signal appears in men, because chronic prostatitis will require more time and money. The modern treatment of prostatitis allows you to cope with any form and stage of the disease, with little impact on the body.
How long does it take to treat prostatitis?
How much prostatitis needs to be treated and whether it can be cured without consequences depends on the complexity of the specific situation. The sooner a person turns to an expert, the better the chance of effective treatment of prostatitis. The treatment time for prostatitis may be 1 to 6 months, depending on the form of the disease. It is worth considering the time spent on diagnosis, which will also affect the treatment time of prostatitis.
How and how to treat
There is no single treatment plan for prostatitis, because this disease is very diverse and requires individualized treatment. However, regardless of its form, the following methods can be used to treat prostatitis:
- medical treatement. . . Antibiotics can be used to treat chronic and acute prostatitis. This is an indispensable part of the treatment of all types of prostatitis. In the acute course of the disease, since it usually takes a long time to treat prostatitis, painkillers are allowed.
- physiotherapy. . . The treatment plan for prostatitis certainly involves physical therapy as a way of lightly massaging the prostate. In addition, herbal enemas and other procedures can be prescribed.
- diet. . . Since it is difficult to cure chronic prostatitis or its acute form with unhealthy intestines, it is necessary to diet or adjust the diet.
- Physical Exercise. . . This method of treating prostatitis is necessary to improve the blood circulation of internal organs.
Prevent prostatitis
In order to avoid prostatitis, you can follow the following simple suggestions either after a previous illness or without such experience:
- Stable sex life. . . Sexual life with a healthy partner can not only avoid sexually transmitted diseases (prostatitis often occurs thereafter), but also avoid stagnation.
- Reject bad habits. . . An unhealthy lifestyle will reduce the body's defenses, so it is best to avoid smoking, drinking alcohol and unhealthy food.
- Sports activities. . . Exercising keeps the body in good condition and improves blood flow to the prostate, thereby reducing the risk of prostatitis.
- Prostate massage. . . This is a measure of secondary prevention of prostatitis for people who already have the disease.
- Preventive agent. . . These are vitamin complexes that can help prevent prostatitis and strengthen the immune system. Use as directed by your doctor.
Prostatitis and pregnancy
Whether the husband may have chronic prostatitis is a problem that worries many families. It must be understood that the prostate is responsible for many of the most important functions related to conception. Therefore, prostatitis increases the possibility of male infertility. The presence of infection and inflammation in the prostate can affect the quality of ejaculation. Although a child who can become pregnant has prostatitis, the chance of success is reduced.
Prostatitis and infertility are closely related, because due to obstruction of the vas deferens, you may not get pregnant after sex. The presence of purulent and bloody secretions in the sperm of men with prostatitis can severely impair its quality and reduce the likelihood of conception.
With prostatitis, you can become pregnant, but to get the best results, you must first cure the disease and prevent possible infertility. Only after a man is cured of prostatitis, will he have time to consider planning a pregnancy. For the treatment of prostatitis and the planning of childbirth, it is best to contact specialized centers, which will definitely help solve all problems.